側彎人之迷思-柔軟度過大?
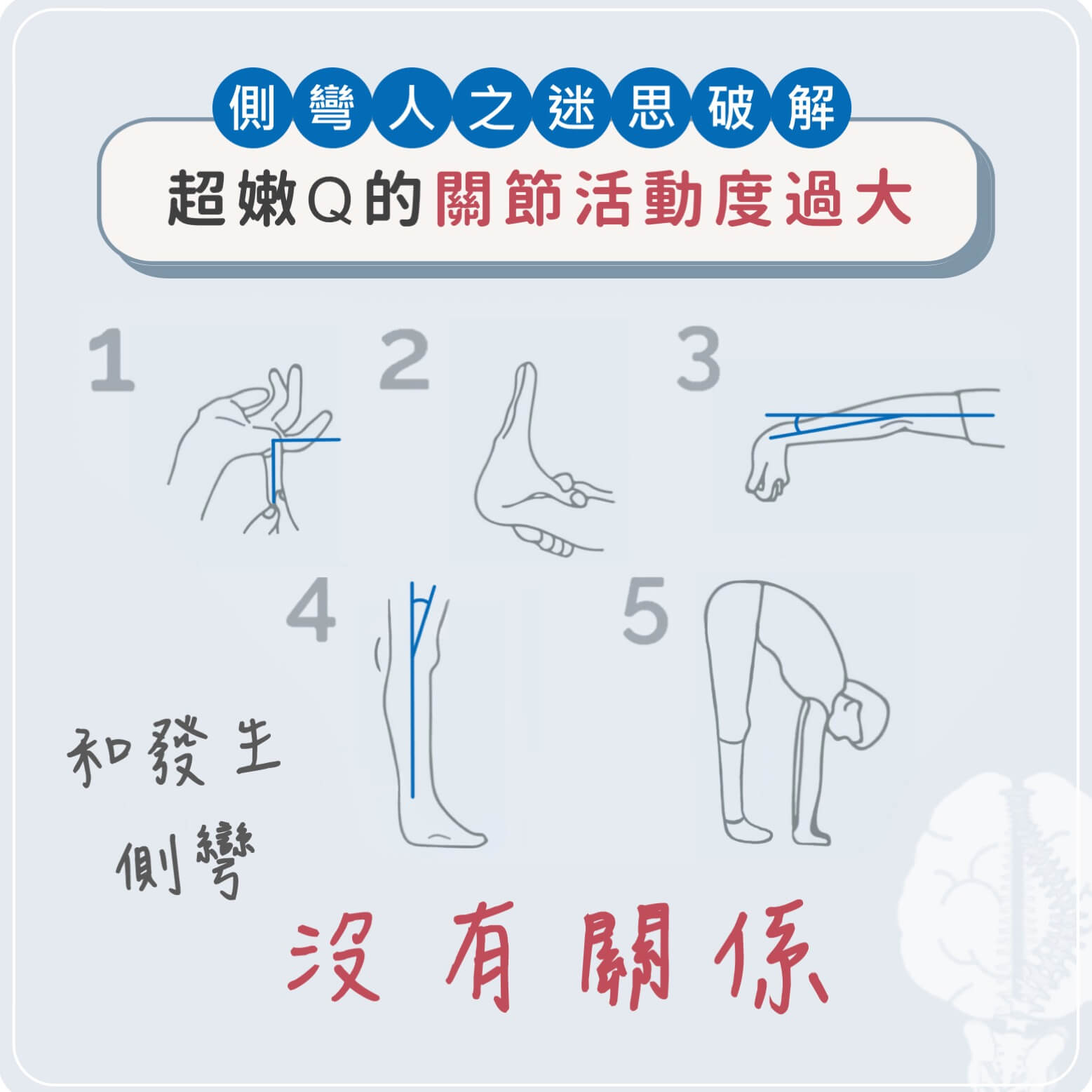
你也有超嫩Q的關節嗎?當關節因為軟組織延展性極高,也就是肌肉、韌帶、關節囊等富有彈性時,活動範圍變得很大,形成字面上的 「關節活動度/柔軟度過大」(俗稱懶骨頭),臨床上常使用的檢測方式為 Beighton Score,若在以下測試得分大於4分則有關節活動度過大 (Generalized Joint Hypermobility, GJH) 情形:
☑️ 小指頭往手背折可以超過 90°(左右手各一分)
☑️ 大拇指往回拉可以碰到前臂(左右手各一分)
☑️ 手肘放鬆伸直時可以往下折 10°(左右手各一分)
☑️ 膝蓋伸直可以往後頂 10°(左右腳各一分)
☑️ 膝蓋伸直身體向前彎時可以整隻手掌碰到地板(一分)
雖然目前脊椎側彎成因不明,仍有許多學者提出關節活動度過大可能為脊椎側彎的形成風險之一,但是綜合許多研究來看,脊椎側彎的青少年似乎有高於一般青少年的關節活動度過大的趨勢,其實大多並沒有統計上的顯著差異。
所以說,很嫩Q不一定會提高發生側彎的風險喔。
參考資料:
1. Dobies-Krześniak BK, Tarnacka B, Werblińska A. Joint hypermobility in school-aged children and adolescents with idiopathic scoliosis – A chance for more accurate screening?. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2022.
2. Haller, Gabe & Zabriskie, Hannah & Spehar, Shelby & Kuensting, Timothy & Bledsoe, Xavier & Syed, Ali & Gurnett, Christina & Dobbs, Matthew. Lack of joint hypermobility increases the risk of surgery in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. J Pediatr Orthop B. 2018; 27(2): 152–158.
3. Maja Fadzan1 and Josette Bettany-Saltikov. Etiological Theories of Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis: Past and Present. The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2017; 11: Suppl-9, M3, 1466-1489.
4. Picture modified from Dr Rowe (https://www.doctorrowe.com/do-you-have-joint-hypermobility-syndrome-start-with-the-beighton-score/)

